Data types in C Language
Data types specify how we enter data into our programs and what type of data we enter. C language has some predefined set of data types to handle various kinds of data that we can use in our program. These datatypes have different storage capacities.
C language supports 2 different type of data types:
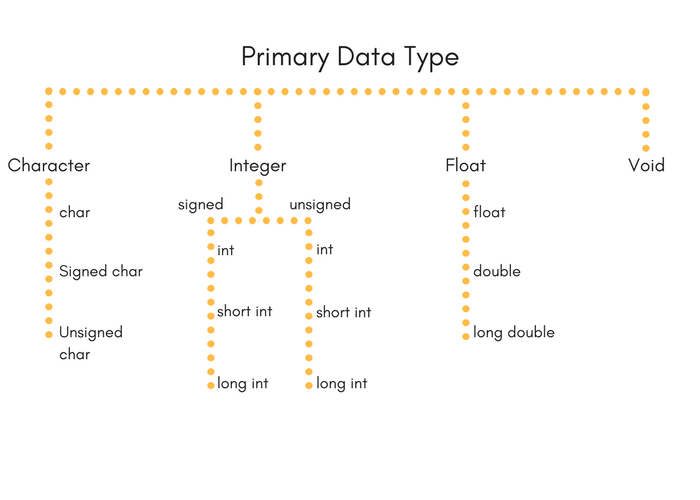
- Primary data types:
These are fundamental data types in C namely integer(int), floating point(float), character(char) and void.
- Derived data types:
Derived data types are nothing but primary datatypes but a little twisted or grouped together like array, stucture, union and pointer. These are discussed in details later.
Data type determines the type of data a variable will hold. If a variable x is declared as int. it means x can hold only integer values. Every variable which is used in the program must be declared as what data-type it is.
Integer type
Integers are used to store whole numbers.
Size and range of Integer type on 16-bit machine:
| Type | Size(bytes) | Range |
|---|
| int or signed int | 2 | -32,768 to 32767 |
| unsigned int | 2 | 0 to 65535 |
| short int or signed short int | 1 | -128 to 127 |
| unsigned short int | 1 | 0 to 255 |
| long int or signed long int | 4 | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| unsigned long int | 4 | 0 to 4,294,967,295 |
Floating point type
Floating types are used to store real numbers.
Size and range of Integer type on 16-bit machine
| Type | Size(bytes) | Range |
|---|
| Float | 4 | 3.4E-38 to 3.4E+38 |
| double | 8 | 1.7E-308 to 1.7E+308 |
| long double | 10 | 3.4E-4932 to 1.1E+4932 |
Character type
Character types are used to store characters value.
Size and range of Integer type on 16-bit machine
| Type | Size(bytes) | Range |
|---|
| char or signed char | 1 | -128 to 127 |
| unsigned char | 1 | 0 to 255 |
void type
void type means no value. This is usually used to specify the type of functions which returns nothing. We will get acquainted to this datatype as we start learning more advanced topics in C language, like functions, pointers etc.
Variables in C Language
When we want to store any information(data) on our computer/laptop, we store it in the computer's memory space. Instead of remembering the complex address of that memory space where we have stored our data, our operating system provides us with an option to create folders, name them, so that it becomes easier for us to find it and access it.
Similarly, in C language, when we want to use some data value in our program, we can store it in a memory space and name the memory space so that it becomes easier to access it.
The naming of an address is known as variable. Variable is the name of memory location. Unlike constant, variables are changeable, we can change value of a variable during execution of a program. A programmer can choose a meaningful variable name. Example : average, height, age, total etc.
Datatype of Variable
A variable in C language must be given a type, which defines what type of data the variable will hold.
It can be:
char: Can hold/store a character in it.int: Used to hold an integer.float: Used to hold a float value.double: Used to hold a double value.void
Rules to name a Variable
- Variable name must not start with a digit.
- Variable name can consist of alphabets, digits and special symbols like underscore
_.
- Blank or spaces are not allowed in variable name.
- Keywords are not allowed as variable name.
- Upper and lower case names are treated as different, as C is case-sensitive, so it is suggested to keep the variable names in lower case.
Declaring, Defining and Initializing a variable
Declaration of variables must be done before they are used in the program. Declaration does the following things.
- It tells the compiler what the variable name is.
- It specifies what type of data the variable will hold.
- Until the variable is defined the compiler doesn't have to worry about allocating memory space to the variable.
- Declaration is more like informing the compiler that there exist a variable with following datatype which is used in the program.
- A variable is declared using the
extern keyword, outside the main() function.
extern int a;
extern float b;
extern double c, d;
Defining a variable means the compiler has to now assign a storage to the variable because it will be used in the program. It is not necessary to declare a variable using extern keyword, if you want to use it in your program. You can directly define a variable inside the main() function and use it.
To define a function we must provide the datatype and the variable name. We can even define multiple variables of same datatype in a single line by using comma to separate them.
int a;
float b, c;
Initializing a variable means to provide it with a value. A variable can be initialized and defined in a single statement, like:
int a = 10;
Let's write a program in which we will use some variables.
#include <stdio.h>
extern int a, b;
extern int c;
int main () {
int a, b;
a = 7;
b = 14;
c = a + b;
printf("Sum is : %d \n", c);
return 0;
}
Sum is : 21
You must be thinking how does this printf() works, right? Do not worry, we will learn about it along with other ways to input and output datain C language in the next tutorial.
Difference between Variable and Identifier?
An Identifier is a name given to any variable, function, structure, pointer or any other entity in a programming language. While a variable, as we have just learned in this tutorial is a named memory location to store data which is used in the program.
| Identifier | Variable |
|---|
| Identifier is the name given to a variable, function etc. | While, variable is used to name a memory location which stores data. |
| An identifier can be a variable, but not all indentifiers are variables. | All variable names are identifiers. |
Example:
int studytonight;
int studytonight() {
..
}
| Example:
int a;
float a;
|
Another great analogy to understand the difference between Identifier and Variable is:
You can think of an Identifier int x to be a variable's name, but it can also be a function's name int x() { } and still be an identifier.
Just like Obama is a name of a person, but also the name of a foundation.

Comments
Post a Comment